Executive functioning refers to the set of mental skills that help individuals manage time, focus attention, plan and organize, and regulate behavior. These cognitive processes are essential for navigating daily life, academic success, and personal relationships. Executive functioning skills begin developing in early childhood and continue to mature into adulthood, playing a key role in how we think, behave, and learn.
In this post, we’ll break down the core components of executive functioning, helping you understand how each one impacts your daily life and offering practical tips for improving them.
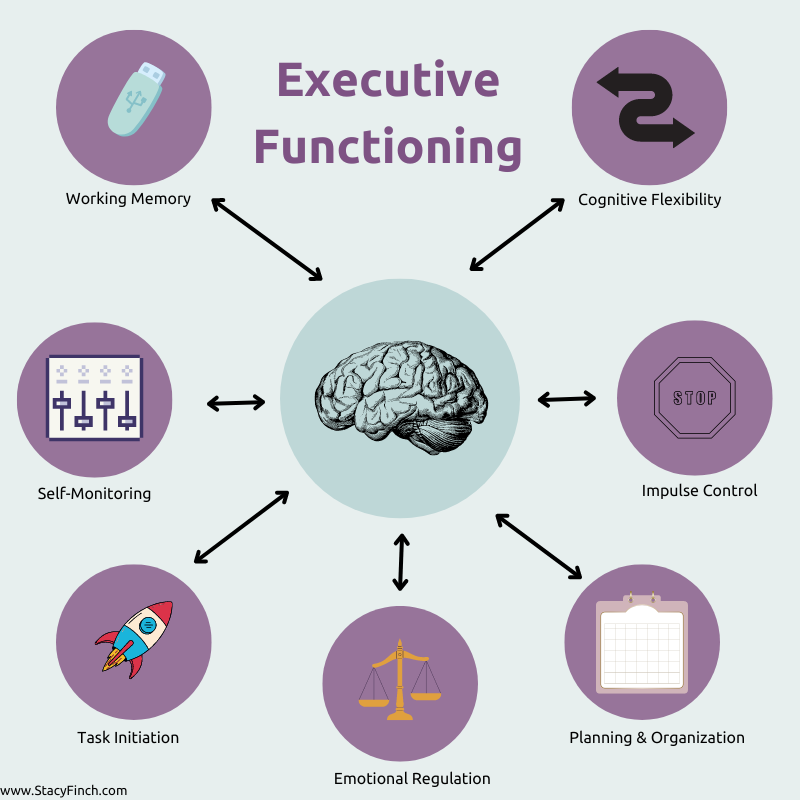
The Core Components of Executive Functioning
- Working Memory
Working memory allows us to hold and manipulate information in our minds over short periods. It’s crucial for following instructions, remembering what we’re doing while multitasking, and problem-solving. For example, working memory helps you retain a phone number long enough to dial it or follow a recipe step by step.
Tip: Practice memory games or use mental visualization techniques to strengthen this skill. Breaking tasks into smaller steps can also make information more manageable. - Cognitive Flexibility
Cognitive flexibility, or flexible thinking, enables us to adapt to new situations, consider alternative solutions, and shift perspectives. It’s essential for problem-solving and creativity. For example, if your commute route is blocked, cognitive flexibility helps you quickly decide on a new path without becoming frustrated.
Tip: Embrace new experiences and challenge yourself to think outside the box. Switching between tasks and looking at problems from multiple angles also enhances flexibility. - Inhibitory Control (Impulse Control)
Inhibitory control refers to the ability to control impulsive behaviors and resist distractions. It helps us make thoughtful decisions rather than acting on immediate desires or emotions. This skill is critical for everything from delaying gratification (e.g., waiting to buy something until it’s on sale) to resisting the temptation to interrupt someone mid-conversation.
Tip: Mindfulness exercises and practicing delayed gratification can help improve inhibitory control. Breaks during focus-intensive tasks are helpful for reducing impulsivity and maintaining self-regulation. - Planning and Organization
Planning and organization are the abilities to set goals, create structured steps, and prioritize tasks. These skills are key for effectively managing time and completing complex projects, such as writing a paper or preparing a presentation. Without a solid plan, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and lost.
Tip: Use planners, calendars, or task management apps to keep track of deadlines and break projects into smaller tasks. Setting aside time each day for organization can help you stay on track. - Task Initiation
Task initiation refers to the ability to start a task without procrastinating. Many people struggle with finding the motivation to begin, especially when faced with complex or unfamiliar projects. Good task initiation helps you overcome that initial hurdle.
Tip: Try the “5-minute rule”: commit to working on a task for just five minutes. Often, starting is the hardest part, and once you’re in motion, it’s easier to keep going. - Self-Monitoring
Self-monitoring involves assessing your performance and adjusting your strategies accordingly. This skill allows you to evaluate your progress toward a goal and make necessary changes. For instance, if you’re studying for an exam, self-monitoring helps you recognize if your study methods are working or if you need to try a different approach.
Tip: Regularly reflect on your performance by asking yourself, “Is this working? What could I do differently?” Self-check-ins help you stay on track and adjust before problems become bigger. - Emotional Regulation
Emotional regulation is the ability to manage and respond to emotions appropriately. It’s critical for maintaining relationships and staying focused under stress. Effective emotional regulation helps prevent emotional outbursts, allows you to cope with challenges, and ensures that emotions don’t interfere with achieving your goals.
Tip: Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to help manage strong emotions. Learning to identify and label your emotions can also reduce their intensity.
Why Executive Functioning Matters
Executive functioning skills are essential for succeeding in both academic and professional environments. These cognitive abilities help you stay organized, adapt to changes, and control emotions—all of which are important for meeting personal and career goals.
For individuals who struggle with executive functioning challenges, such as those with ADHD or other neurodevelopmental conditions, support can be critical. Executive dysfunction can lead to issues with time management, problem-solving, and emotional control, but with the right strategies and tools, these challenges can be overcome.
Take the Next Step
If you or a loved one is struggling with executive functioning challenges, I can help. Through personalized coaching and support, we can work together to build and strengthen these skills, helping you lead a more organized and successful life.
Schedule a session today to start making positive changes!

0 Comments